并查集 size 的优化
按照上一小节的思路,我们把如下图所示的并查集,进行 union(4,9) 操作。
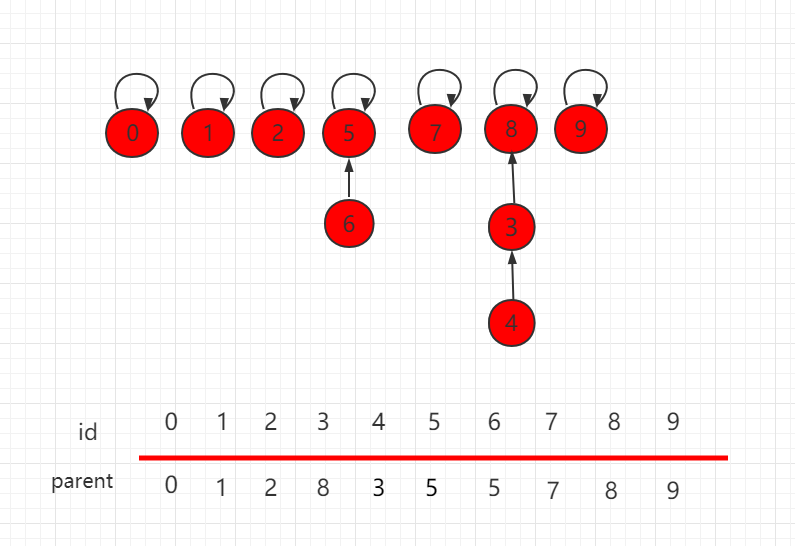
合并操作后的结构为:
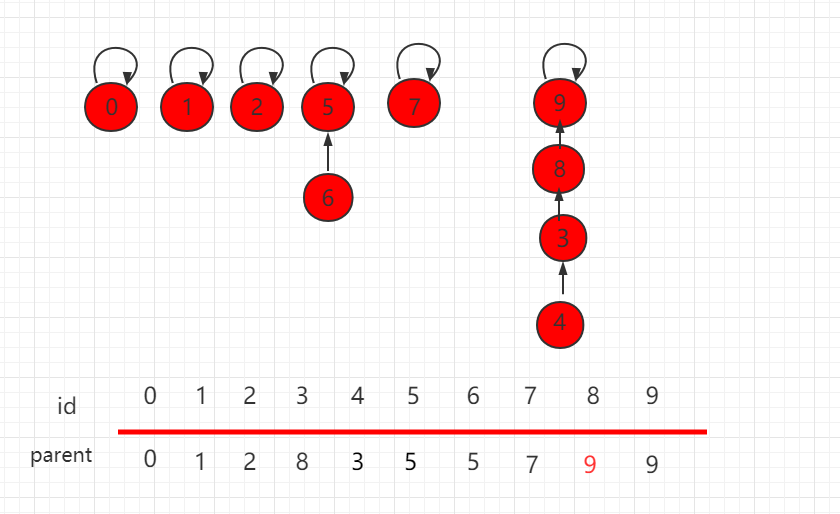
可以发现,这个结构的树的层相对较高,若此时元素数量增多,这样产生的消耗就会相对较大。解决这个问题其实很简单,在进行具体指向操作的时候先进行判断,把元素少的集合根节点指向元素多的根节点,能更高概率的生成一个层数比较低的树。
构造并查集的时候需要多一个参数,sz 数组,sz[i] 表示以 i 为根的集合中元素个数。
// 构造函数
public UnionFind3(int count){
parent = new int[count];
sz = new int[count];
this.count = count;
// 初始化, 每一个parent[i]指向自己, 表示每一个元素自己自成一个集合
for( int i = 0 ; i < count ; i ++ ){
parent[i] = i;
sz[i] = 1;
}
}
public UnionFind3(int count){
parent = new int[count];
sz = new int[count];
this.count = count;
// 初始化, 每一个parent[i]指向自己, 表示每一个元素自己自成一个集合
for( int i = 0 ; i < count ; i ++ ){
parent[i] = i;
sz[i] = 1;
}
}
在进行合并操作时候,根据两个元素所在树的元素个数不同判断合并方向。
public void unionElements(int p, int q){
int pRoot = find(p);
int qRoot = find(q);
if( pRoot == qRoot )
return;
if( sz[pRoot] < sz[qRoot] ){
parent[pRoot] = qRoot;
sz[qRoot] += sz[pRoot];
}
else{
parent[qRoot] = pRoot;
sz[pRoot] += sz[qRoot];
}
}
int pRoot = find(p);
int qRoot = find(q);
if( pRoot == qRoot )
return;
if( sz[pRoot] < sz[qRoot] ){
parent[pRoot] = qRoot;
sz[qRoot] += sz[pRoot];
}
else{
parent[qRoot] = pRoot;
sz[pRoot] += sz[qRoot];
}
}
优化后,合并结果如下,9 指向父节点 8。
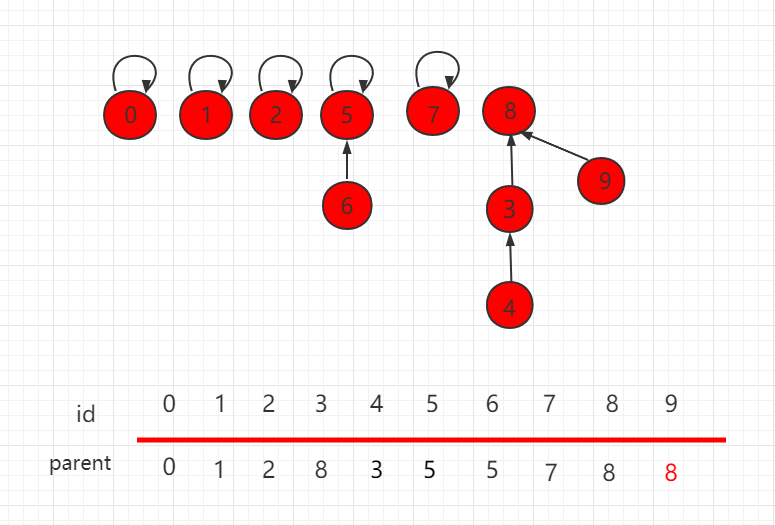
Java 实例代码
源码包下载:Download
UnionFind3.java 文件代码:
package runoob.union;
/**
* 并查集size的优化
*/
public class UnionFind3 {
// parent[i]表示第一个元素所指向的父节点
private int[] parent;
// sz[i]表示以i为根的集合中元素个数
private int[] sz;
// 数据个数
private int count;
// 构造函数
public UnionFind3(int count){
parent = new int[count];
sz = new int[count];
this.count = count;
// 初始化, 每一个parent[i]指向自己, 表示每一个元素自己自成一个集合
for( int i = 0 ; i < count ; i ++ ){
parent[i] = i;
sz[i] = 1;
}
}
// 查找过程, 查找元素p所对应的集合编号
// O(h)复杂度, h为树的高度
private int find(int p){
assert( p >= 0 && p < count );
// 不断去查询自己的父亲节点, 直到到达根节点
// 根节点的特点: parent[p] == p
while( p != parent[p] )
p = parent[p];
return p;
}
// 查看元素p和元素q是否所属一个集合
// O(h)复杂度, h为树的高度
public boolean isConnected( int p , int q ){
return find(p) == find(q);
}
// 合并元素p和元素q所属的集合
// O(h)复杂度, h为树的高度
public void unionElements(int p, int q){
int pRoot = find(p);
int qRoot = find(q);
if( pRoot == qRoot )
return;
// 根据两个元素所在树的元素个数不同判断合并方向
// 将元素个数少的集合合并到元素个数多的集合上
if( sz[pRoot] < sz[qRoot] ){
parent[pRoot] = qRoot;
sz[qRoot] += sz[pRoot];
}
else{
parent[qRoot] = pRoot;
sz[pRoot] += sz[qRoot];
}
}
}
/**
* 并查集size的优化
*/
public class UnionFind3 {
// parent[i]表示第一个元素所指向的父节点
private int[] parent;
// sz[i]表示以i为根的集合中元素个数
private int[] sz;
// 数据个数
private int count;
// 构造函数
public UnionFind3(int count){
parent = new int[count];
sz = new int[count];
this.count = count;
// 初始化, 每一个parent[i]指向自己, 表示每一个元素自己自成一个集合
for( int i = 0 ; i < count ; i ++ ){
parent[i] = i;
sz[i] = 1;
}
}
// 查找过程, 查找元素p所对应的集合编号
// O(h)复杂度, h为树的高度
private int find(int p){
assert( p >= 0 && p < count );
// 不断去查询自己的父亲节点, 直到到达根节点
// 根节点的特点: parent[p] == p
while( p != parent[p] )
p = parent[p];
return p;
}
// 查看元素p和元素q是否所属一个集合
// O(h)复杂度, h为树的高度
public boolean isConnected( int p , int q ){
return find(p) == find(q);
}
// 合并元素p和元素q所属的集合
// O(h)复杂度, h为树的高度
public void unionElements(int p, int q){
int pRoot = find(p);
int qRoot = find(q);
if( pRoot == qRoot )
return;
// 根据两个元素所在树的元素个数不同判断合并方向
// 将元素个数少的集合合并到元素个数多的集合上
if( sz[pRoot] < sz[qRoot] ){
parent[pRoot] = qRoot;
sz[qRoot] += sz[pRoot];
}
else{
parent[qRoot] = pRoot;
sz[pRoot] += sz[qRoot];
}
}
}

点我分享笔记